After you have set up a GAA, you generally figure the MACRS depreciation for it by using the applicable depreciation method, recovery period, and convention for the property in the GAA. For each GAA, record the depreciation allowance in a separate depreciation reserve account. Under MACRS, Tara is allowed 4 months of depreciation for the short tax year that consists of 10 months. The corporation first multiplies the basis ($1,000) by 40% to get the depreciation for a full tax year of $400. The corporation then multiplies $400 by 4/12 to get the short tax year depreciation of $133.
Create a Free Account and Ask Any Financial Question
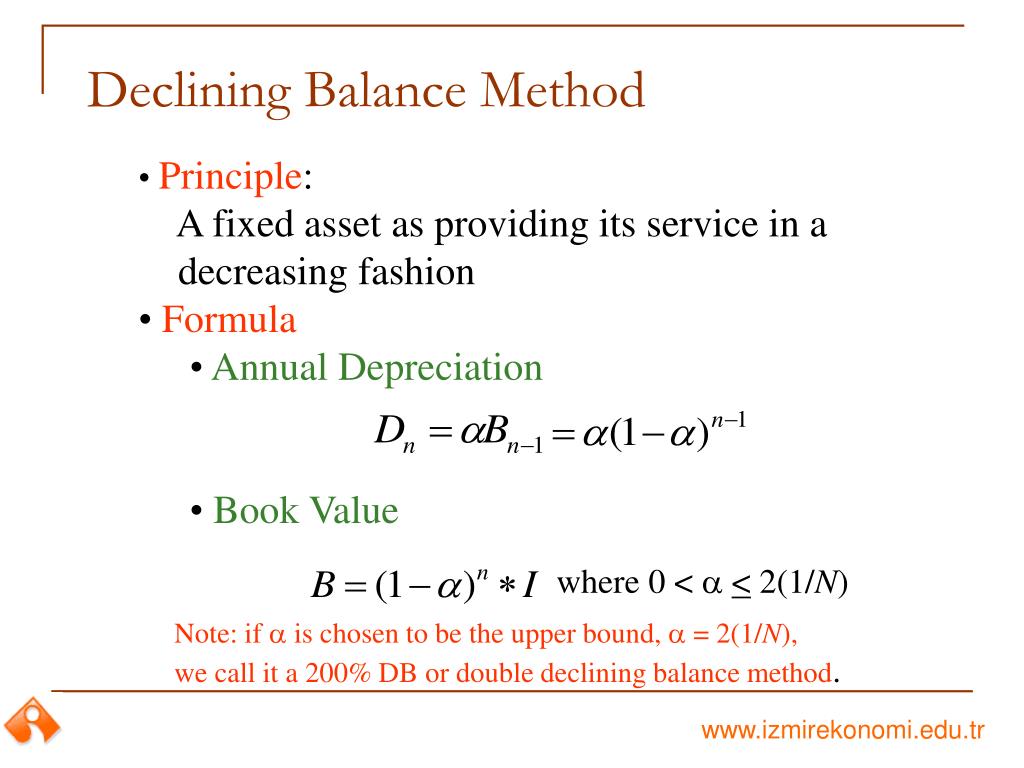
The book value, or depreciation base, of an asset, declines over time. The following examples show the application of the double and 150% declining balance methods to calculate asset depreciation. The double-declining method involves depreciating an asset more heavily in the early years of its useful life. A business might write off $3,000 of an asset valued at $5,000 in the first year rather than $1,000 a year for five years as with straight-line depreciation. The double-declining method depreciates assets twice as quickly as the declining balance method as the name suggests.
Double-Declining Balance (DDB) Depreciation Method Definition With Formula
Expenses generally paid by a buyer to research the title of real property. You can use Schedule LEP (Form 1040), Request for Change in Language Preference, to state a preference to receive notices, letters, or other written communications from the IRS in an alternative language. You may not immediately receive written communications in the requested language.
- To be depreciable, property must have a useful life that extends substantially beyond the year you place it in service.
- Suppose you purchase an asset for your business for $575,000 and you expect it to have a life of 10 years with a final salvage value of $5,000.
- It elects to expense the entire $1,160,000 cost under section 179.
- However, if you buy technical books, journals, or information services for use in your business that have a useful life of 1 year or less, you cannot depreciate them.
- You placed property in service during the last 3 months of the year, so you must first determine if you have to use the mid-quarter convention.
Step 4: Compute Final Year Depreciation Expense
The following examples show how to figure depreciation under MACRS without using the percentage tables. Assume for all the examples that you use a calendar year as your tax year. If you elect not to apply the uniform capitalization rules to any plant produced in your farming business, you must use ADS. You must use ADS for all property you place in service in any year the election is in effect. See the regulations under section 263A of the Internal Revenue Code for information on the uniform capitalization rules that apply to farm property. Depreciate trees and vines bearing fruits or nuts under GDS using the straight line method over a recovery period of 10 years.

Calculate declining balance depreciation
Qualified reuse and recycling property does not include any of the following. You must keep records that show the specific identification of each piece of qualifying section 179 property. These records must show how you acquired the property, the person you acquired it from, and when you placed it in service.
Differences Between Straight Line Method and Declining Balance Method
The numerator of the fraction is the number of days in the lease term, and the denominator is 365 (or 366 for leap years). The business-use requirement generally does not apply to any listed property leased or held for leasing by anyone regularly engaged in the business of leasing listed property. Whether the use of listed property is for your employer’s convenience must be determined from all the facts.
Appendix A contains the MACRS Percentage Table Guide, which is designed to help you locate the correct percentage table to use for depreciating your property. However, a qualified improvement does not include any improvement for which the expenditure is attributable to any of the following. If you placed your property in service in 2023, complete Part III of Form 4562 to report depreciation using MACRS. Complete Section B of Part III to report depreciation using GDS, and complete Section C of Part III to report depreciation using ADS.
Depreciation allows a company to deduct an asset’s declining value, reducing the amount of income on which it must pay taxes. Its anticipated service life must be for more than one year and it must have a determinable useful life expectancy. The amount of final year depreciation will equal the difference between the book value of the laptop at the risk response plan start of the accounting period ($218.75) and the asset’s salvage value ($200). For example, if an asset has a useful life of 10 years (i.e., Straight-line rate of 10%), the depreciation rate of 20% would be charged on its carrying value. Using this new, longer time frame, depreciation will now be $5,250 per year, instead of the original $9,000.
May used the property 80% for business and 20% for personal purposes. The business part of the cost of the property is $8,800 (80% (0.80) × $11,000). Do not use Form 4562 if you are an employee and you deduct job-related vehicle expenses using either actual expenses (including depreciation) or the standard mileage rate. If you do not claim depreciation you are entitled to deduct, you must still reduce the basis of the property by the full amount of depreciation allowable. If you construct, build, or otherwise produce property for use in your business, you may have to use the uniform capitalization rules to determine the basis of your property. For information about the uniform capitalization rules, see Pub.


